How To Work Bullshit Jobs
What David Graeber's 2013 essay "On the Phenomenon of Bullshit Jobs" gets right and wrong about the Professional Managerial Class
Comrades: The era of bullshit jobs is ending.
In 2013, economic anthropologist David Graeber penned a seminal essay about Bullshit Jobs. He nailed the farce of the institutionalized PMC NPC: Professional Managerial Class Non-Player Character. A decade later, the illusions of the PMC are disintegrating as AI is threatens to automate many of their BS jobs. However, Graeber misses several important points because he was a member of the limousine Marxist class - institutionalized, not instinctual. He passed away in 2020 before he could see his prophecy come to fruition in the post-COVID world. Let’s reexamine how his words have aged.
In the year 1930, John Maynard Keynes predicted that, by century's end, technology would have advanced sufficiently that countries like Great Britain or the United States would have achieved a 15-hour work week. There's every reason to believe he was right. In technological terms, we are quite capable of this. And yet it didn't happen. Instead, technology has been marshaled, if anything, to figure out ways to make us all work more. In order to achieve this, jobs have had to be created that are, effectively, pointless. Huge swathes of people, in Europe and North America in particular, spend their entire working lives performing tasks they secretly believe do not really need to be performed. The moral and spiritual damage that comes from this situation is profound. It is a scar across our collective soul. Yet virtually no one talks about it.
Keynes was right. Most bullshit jobs only require 15 hours of real work per week. Technology has been marshaled to create the illusion of work. E-mails, Slack messages, Zoom meetings, etc. allow pointless workers to hold pointless meetings ad infinitum. COVID exposed this system when the laptop class worked from home, while essential workers reported for duty to keep society running.
Why did Keynes' promised utopia—still being eagerly awaited in the '60s—never materialise? The standard line today is that he didn't figure in the massive increase in consumerism. Given the choice between less hours and more toys and pleasures, we've collectively chosen the latter. This presents a nice morality tale, but even a moment's reflection shows it can't really be true. Yes, we have witnessed the creation of an endless variety of new jobs and industries since the '20s, but very few have anything to do with the production and distribution of sushi, iPhones, or fancy sneakers.
So what are these new jobs, precisely? A recent report comparing employment in the US between 1910 and 2000 gives us a clear picture (and I note, one pretty much exactly echoed in the UK). Over the course of the last century, the number of workers employed as domestic servants, in industry, and in the farm sector has collapsed dramatically. At the same time, ‘professional, managerial, clerical, sales, and service workers’ tripled, growing ‘from one-quarter to three-quarters of total employment.’ In other words, productive jobs have, just as predicted, been largely automated away (even if you count industrial workers globally, including the toiling masses in India and China, such workers are still not nearly so large a percentage of the world population as they used to be.)
Rising inflation and taxes due to leftist government policies have kept the masses on the consumption hamster wheel. Around half of all Americans are on welfare or live paycheck to paycheck. New jobs and industries have boosted productivity, but most of the gains have accrued to globalist executives and shareholders instead of workers. Middle management BS jobs at corporations involve all the laptop work behind financing, advertising, and selling sushi, iPhones, and sneakers. The real production and distribution work was outsourced to cheap labor in China and India, while mass migration drove down lower/middle-class wages in America. AI is taking automation to the next level.
But rather than allowing a massive reduction of working hours to free the world's population to pursue their own projects, pleasures, visions, and ideas, we have seen the ballooning of not even so much of the ‘service’ sector as of the administrative sector, up to and including the creation of whole new industries like financial services or telemarketing, or the unprecedented expansion of sectors like corporate law, academic and health administration, human resources, and public relations. And these numbers do not even reflect on all those people whose job is to provide administrative, technical, or security support for these industries, or for that matter the whole host of ancillary industries (dog-washers, all-night pizza delivery) that only exist because everyone else is spending so much of their time working in all the other ones. These are what I propose to call ‘bullshit jobs’.
It's as if someone were out there making up pointless jobs just for the sake of keeping us all working. And here, precisely, lies the mystery. In capitalism, this is precisely what is not supposed to happen. Sure, in the old inefficient socialist states like the Soviet Union, where employment was considered both a right and a sacred duty, the system made up as many jobs as they had to (this is why in Soviet department stores it took three clerks to sell a piece of meat). But, of course, this is the sort of very problem market competition is supposed to fix. According to economic theory, at least, the last thing a profit-seeking firm is going to do is shell out money to workers they don't really need to employ. Still, somehow, it happens.
Bullshit jobs arose from cronyism, not capitalism. DEI/ESG Commissars and patronage networks have metastasized administrative bloat across for-profit and non-profit entities. Elon’s acquisition of X proved that the majority of workers at most large institutions are doing BS. Organizations can not only survive major cuts, but grow stronger. DOGE has started putting many commissars out of the misery of their miserable bullshit jobs, which have harmed society on so many levels.
How To Fire a Commissar
Comrades: Administrative bloat in education and healthcare is the real pandemic.
While corporations may engage in ruthless downsizing, the layoffs and speed-ups invariably fall on that class of people who are actually making, moving, fixing and maintaining things; through some strange alchemy no one can quite explain, the number of salaried paper-pushers ultimately seems to expand, and more and more employees find themselves, not unlike Soviet workers actually, working 40 or even 50 hour weeks on paper, but effectively working 15 hours just as Keynes predicted, since the rest of their time is spent organizing or attending motivational seminars, updating their facebook profiles or downloading TV box-sets.
The answer clearly isn't economic: it's moral and political. The ruling class has figured out that a happy and productive population with free time on their hands is a mortal danger (think of what started to happen when this even began to be approximated in the '60s). And, on the other hand, the feeling that work is a moral value in itself, and that anyone not willing to submit themselves to some kind of intense work discipline for most of their waking hours deserves nothing, is extraordinarily convenient for them.
White collar jobs are even more at risk than blue collars jobs in the age of AI. LinkedIn flexing is a cringe side hustle. Idle hands are the devil’s workshop and COVID proved that UBI would not make people more creative or satisfied. We do need to keep the population occupied to prevent social unrest. Graeber never had children of his own, so he has a blind spot on where people spend time and find purpose outside of work.
The decline in fertility rates have exacerbated unhappiness because workers without families are atomized and lonely. Many PMCs are stuck in the hamster wheel rat race trying to striver claw their way to higher paying, more prestigious bullshit jobs instead of having more kids. The most miserable period of my life was when I worked a bullshit job without God or family anchoring me at home (more on that in a future post). Only a generation ago, a single income on a real job could support a family but now dual income BS jobs are required to live in a decent area.
Once, when contemplating the apparently endless growth of administrative responsibilities in British academic departments, I came up with one possible vision of hell. Hell is a collection of individuals who are spending the bulk of their time working on a task they don't like and are not especially good at. Say they were hired because they were excellent cabinet-makers, and then discover they are expected to spend a great deal of their time frying fish. Neither does the task really need to be done—at least, there's only a very limited number of fish that need to be fried. Yet somehow, they all become so obsessed with resentment at the thought that some of their co-workers might be spending more time making cabinets, and not doing their fair share of the fish-frying responsibilities, that before long there's endless piles of useless badly cooked fish piling up all over the workshop and it's all that anyone really does. I think this is actually a pretty accurate description of the moral dynamics of our own economy.
University administrators have saddled a generation with debt from useless degrees. Hell is a collection of Africana studies majors becoming DEI commissars and English majors becoming Starbucks baristas. They resent anyone who is happy and doing real work, which they know deep down that they are not.
Now, I realise any such argument is going to run into immediate objections: ‘who are you to say what jobs are really “necessary”? What's necessary anyway? You're an anthropology professor, what's the “need” for that?’ (And indeed a lot of tabloid readers would take the existence of my job as the very definition of wasteful social expenditure.) And on one level, this is obviously true. There can be no objective measure of social value.
I would not presume to tell someone who is convinced they are making a meaningful contribution to the world that, really, they are not. But what about those people who are themselves convinced their jobs are meaningless? Not long ago I got back in touch with a school friend who I hadn't seen since I was 12. I was amazed to discover that in the interim, he had become first a poet, then the front man in an indie rock band. I'd heard some of his songs on the radio having no idea the singer was someone I actually knew. He was obviously brilliant, innovative, and his work had unquestionably brightened and improved the lives of people all over the world. Yet, after a couple of unsuccessful albums, he'd lost his contract, and plagued with debts and a newborn daughter, ended up, as he put it, ‘taking the default choice of so many directionless folk: law school.’ Now he's a corporate lawyer working in a prominent New York firm. He was the first to admit that his job was utterly meaningless, contributed nothing to the world, and, in his own estimation, should not really exist.
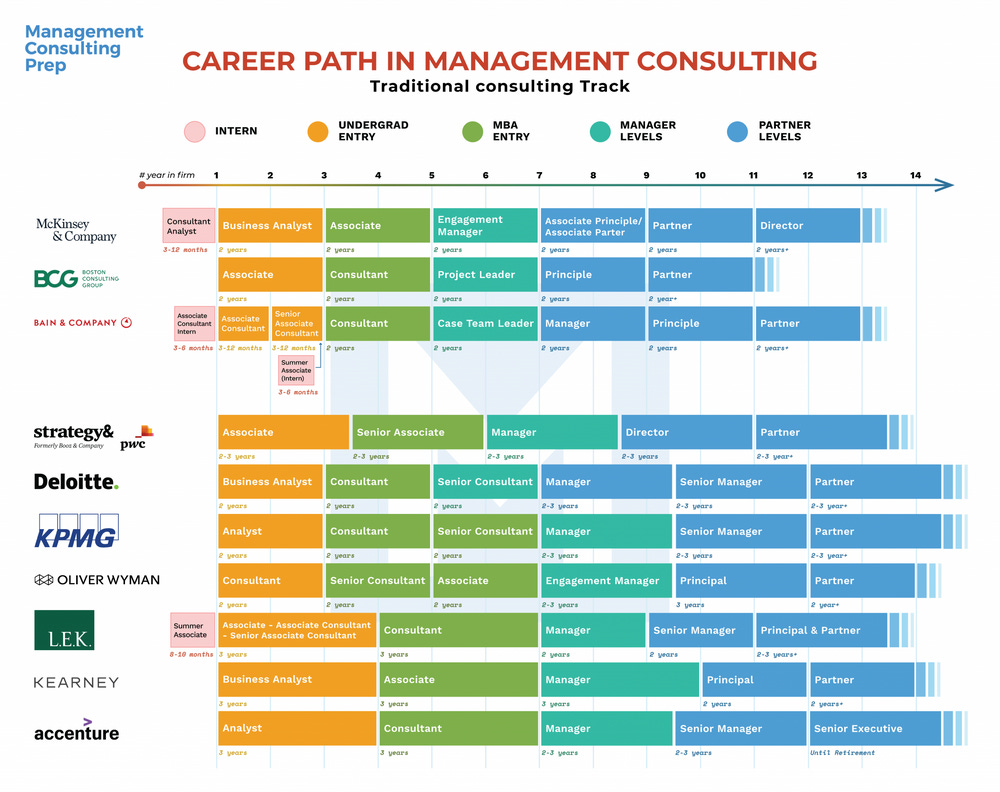
Most humanities professors have negative social value. The Ivy League is full of sellouts like his friend. Investment banks, consulting firms, and big tech companies lure our best and brightest strivers into meaningless bullshit careers. This phenomenon has also resulted in a brain drain from the country into a handful of coastal cities. How many talented people would be more fully actualized if they stuck to their passions instead of getting sucked into the PMC matrix?
How To Hire a PMC Assassin: Professional Managerial Class McKinsey Consultant vs Private Military Company Wagner Mercenary
Comrades: What do an American consulting firm and Russian mercenary group have in common? Much more than you’d think. Join me on this classic Yuri thought exercise.
There's a lot of questions one could ask here, starting with, what does it say about our society that it seems to generate an extremely limited demand for talented poet-musicians, but an apparently infinite demand for specialists in corporate law? (Answer: if 1% of the population controls most of the disposable wealth, what we call ‘the market’ reflects what they think is useful or important, not anybody else.) But even more, it shows that most people in these jobs are ultimately aware of it. In fact, I'm not sure I've ever met a corporate lawyer who didn't think their job was bullshit. The same goes for almost all the new industries outlined above. There is a whole class of salaried professionals that, should you meet them at parties and admit that you do something that might be considered interesting (an anthropologist, for example), will want to avoid even discussing their line of work entirely (one or t'other?) Give them a few drinks, and they will launch into tirades about how pointless and stupid their job really is.
Most bullshit job workers rely on alcohol and other drugs to get them through the numbness of their lives. The power law is brutal. Our society has high demand for talented poet-musicians, but only the top performers make enough income to thrive. Office Space and American Psycho captured the farcical soullessness of corporate office culture.
How To Reimagine the Office Psycho
Comrades: PMC (Professional Managerial Class) NPC (Non Player Character) corporate culture is the institutionalization of demoralization.
This is a profound psychological violence here. How can one even begin to speak of dignity in labour when one secretly feels one's job should not exist? How can it not create a sense of deep rage and resentment. Yet it is the peculiar genius of our society that its rulers have figured out a way, as in the case of the fish-fryers, to ensure that rage is directed precisely against those who actually do get to do meaningful work. For instance: in our society, there seems a general rule that, the more obviously one's work benefits other people, the less one is likely to be paid for it. Again, an objective measure is hard to find, but one easy way to get a sense is to ask: what would happen were this entire class of people to simply disappear? Say what you like about nurses, garbage collectors, or mechanics, it's obvious that were they to vanish in a puff of smoke, the results would be immediate and catastrophic. A world without teachers or dock-workers would soon be in trouble, and even one without science fiction writers or ska musicians would clearly be a lesser place. It's not entirely clear how humanity would suffer were all private equity CEOs, lobbyists, PR researchers, actuaries, telemarketers, bailiffs or legal consultants to similarly vanish. (Many suspect it might markedly improve.) Yet apart from a handful of well-touted exceptions (doctors), the rule holds surprisingly well.
Teachers and doctors destroyed their credibility during COVID. Public schools are a make-work job for leftists to babysit and indoctrinate children of parents who prioritize their bullshit jobs over raising them. We must break this cycle before it destroys our society.
How To Outsource Parenthood
Comrades: America has outsourced its economy and many Americans have outsourced parenthood.
Even more perverse, there seems to be a broad sense that this is the way things should be. This is one of the secret strengths of right-wing populism. You can see it when tabloids whip up resentment against tube workers for paralysing London during contract disputes: the very fact that tube workers can paralyse London shows that their work is actually necessary, but this seems to be precisely what annoys people. It's even clearer in the US, where Republicans have had remarkable success mobilizing resentment against school teachers, or auto workers (and not, significantly, against the school administrators or auto industry managers who actually cause the problems) for their supposedly bloated wages and benefits. It's as if they are being told ‘but you get to teach children! Or make cars! You get to have real jobs! And on top of that you have the nerve to also expect middle-class pensions and health care?’
No one resents real workers. Populism has exposed the managerial class as destructive overhead that has driven up prices while reducing quality. Teachers’ union leaders like Randi Weingarten and her fellow ideologues are the problem. Test scores are at record lows, while education costs are at record highs. The same applies to any union leaders who shake down companies for their own benefit, while workers’ benefits remain stagnant. Ironically, many auto workers’ unions have taken in many bullshit administrative workers.
If someone had designed a work regime perfectly suited to maintaining the power of finance capital, it's hard to see how they could have done a better job. Real, productive workers are relentlessly squeezed and exploited. The remainder are divided between a terrorised stratum of the universally reviled unemployed, and a larger stratum who are basically paid to do nothing, in positions designed to make them identify with the perspectives and sensibilities of the ruling class (managers, administrators, etc.)—and particularly its financial avatars—but, at the same time, foster a simmering resentment against anyone whose work has clear and undeniable social value. Clearly, the system was never consciously designed. It emerged from almost a century of trial and error. But it is the only explanation for why, despite our technological capacities, we are not all working 3–4 hour days.
Graeber concludes with a socialist rant. He uses the word resentment 5 times, which is the core of his ideologies. Bullshit Jobs is one of the best essays written by a leftist, but that is equivalent to winning the special olympics. Productive workers are not resented. As in many cases, the left has manipulated language to argue that many of their bullshit jobs across the public, private, and “non-profit” sectors are productive when they are anything but. “Finance capital” has captured “liberal” parties across the West and many billionaires are the patrons of open borders politicians and NGOs. The populist right advocates for a stronger middle class with lower taxes, inflation, and immigration. Let us keep working towards a system where we can control the hours and terms of our work, while flourishing under a real capitalist and merit-driven society. We need to build stuff, not bull shit.
Frank Sobotka from The Wire summarized BS jobs:














The overproduction of elites - educating our dumb little children - is part of the problem. If you take a four-year course and get a degree in grievance studies, you have to go out there and do something with that newfound knowledge. The fact that what you do fucks everything up is no consequence. In fact it is never even reviewed.
We lost our industrial jobs so we sent Junior to college for education in human resources. Now we have a bunch of losers - junior -!running things and every thing is broken.
As the parent of three young kids in a hardcore striver town, the holy grail of human existence seems to be playing division 3 sports at an elite east coast liberal arts college followed by a career in IB, PE, or CRE. I understand how this can be a fulfilling path for certain alpha male types but I really don't want that life for my kids unless they really want it.
I worked in a hard core bull shit job for like 4 years after law school and came to many of Graeber's conclusions on my own. I was amazed by how many people thrive in that environment and love playing the political corporate game. Despite hating my life during those years, I'm grateful for the experience because working a demanding shitty job for some period of time builds character, but can also fortify your resolve to carve your own path in life. Nowadays I see the commuters going into the city and get a pit in my stomach to work harder on my own flexible and enjoyable business. I honestly think I'd have a breakdown if I had to go back to that life in my 40s.
Although I have plenty of friends, that are, again, absolutely thriving in the corporate world and seem to have plenty of time to do the things they like.